Gearboxes, as part of power transmission systems, are an integral and critical component of conveyor systems, stackers, feeders, and process machinery that help move bulk products. They are used across agriculture, aggregate, material handling, and manufacturing sectors, to name but a few. In this short article, I’ll touch on the conditions that cause equipment failure and costly downtime. I’ll also look at measures that can be taken by plant and facility owners or their equipment suppliers to reduce downtime.
Understanding Equipment Failures Due to Demanding Conditions
Aggregate is one of the most demanding industrial markets, where operations mine, quarry, and manufacture raw materials. Long operating hours, severe shock loading, and extreme weather conditions punish the conveyors, equipment, and machinery used to move bulk materials and process products. Couple these conditions with caustic moisture and damaging contamination, and equipment eventually fails, bringing productivity to a stop and causing costly downtime. Other applications may not be as intense as aggregates, but they each have specific conditions that cause equipment to fail, and no manufacturer’s equipment is immune to this abuse.
Reduce the Probability of Failure by Properly Specifying Equipment.
I would be remiss to understate the importance of correctly matching the gearbox and motor to the severity of the application. The Class of Service and Service Factor are important when selecting power transmission components. To continue my example from above, operating hours, shock loading, and the number of cycles are all important considerations when specifying gearboxes and the conveyor power transmission system as a whole.
Saving money by taking shortcuts and undersizing equipment may reduce initial acquisition costs. These savings are minuscule compared to the costs of a reduction in productivity incurred by the downtime and equipment replacement costs. Undersized or improperly selected system components, such as a single gearbox, could result in replacing an entire power transmission system. So again, underspecifying a gearbox can significantly contribute to equipment failure as any extreme environmental or operating condition.
“Over many years, gearbox manufacturers have developed a methodology and an intelligent approach to product development to minimize unexpected downtime, increase gearboxes’ longevity, and thereby increase productivity.”
A Smart Approach to Equipment Rationalization
Any manufacturing plant or production facility that needs to move bulk materials does so with scores of radial stacker conveyors and feeders in different shapes and sizes. Both power transmission system manufacturers and plant operators recognized that commonality and continuity of systems offer a means to minimize expensive critical spares; this was especially true in the case of gear reducers. If a plant can specify fewer varieties and styles of gearboxes, it can stock spare gearboxes and accessories more affordably to combat unanticipated equipment failures.
The Versatility of Shaft Mount Reducers
Plant operators and manufacturers utilized equipment commonality to develop the Hollow-bore or Shaft-mount gearbox, which is predominantly used today on bulk material handling equipment.
Unlike gearboxes that have a specific fixed ratio or output RPM, Shaft-mount gearboxes incorporate the use of sheaves, bushings, and v-belts to offer flexibility in output speed by coupling the prime mover (electric motor) to the gearbox as the first stage of reduction before the fixed ratio of the reducer (see fig. A).
Each accessory amplifies the simplicity of the system components, enabling gearbox manufacturers to offer fewer enclosures (case sizes) and far fewer ratios—15:1 and 25:1 being the most common among this genre of gear reducers. Furthermore, interchangeable output bushings can be used on Shaft-mount gearboxes, enabling a standard gearbox size to mount onto different conveyor head-shaft diameters (see fig. B). But with this simplicity comes the complexity of specifying the correct combination of components for any given application.
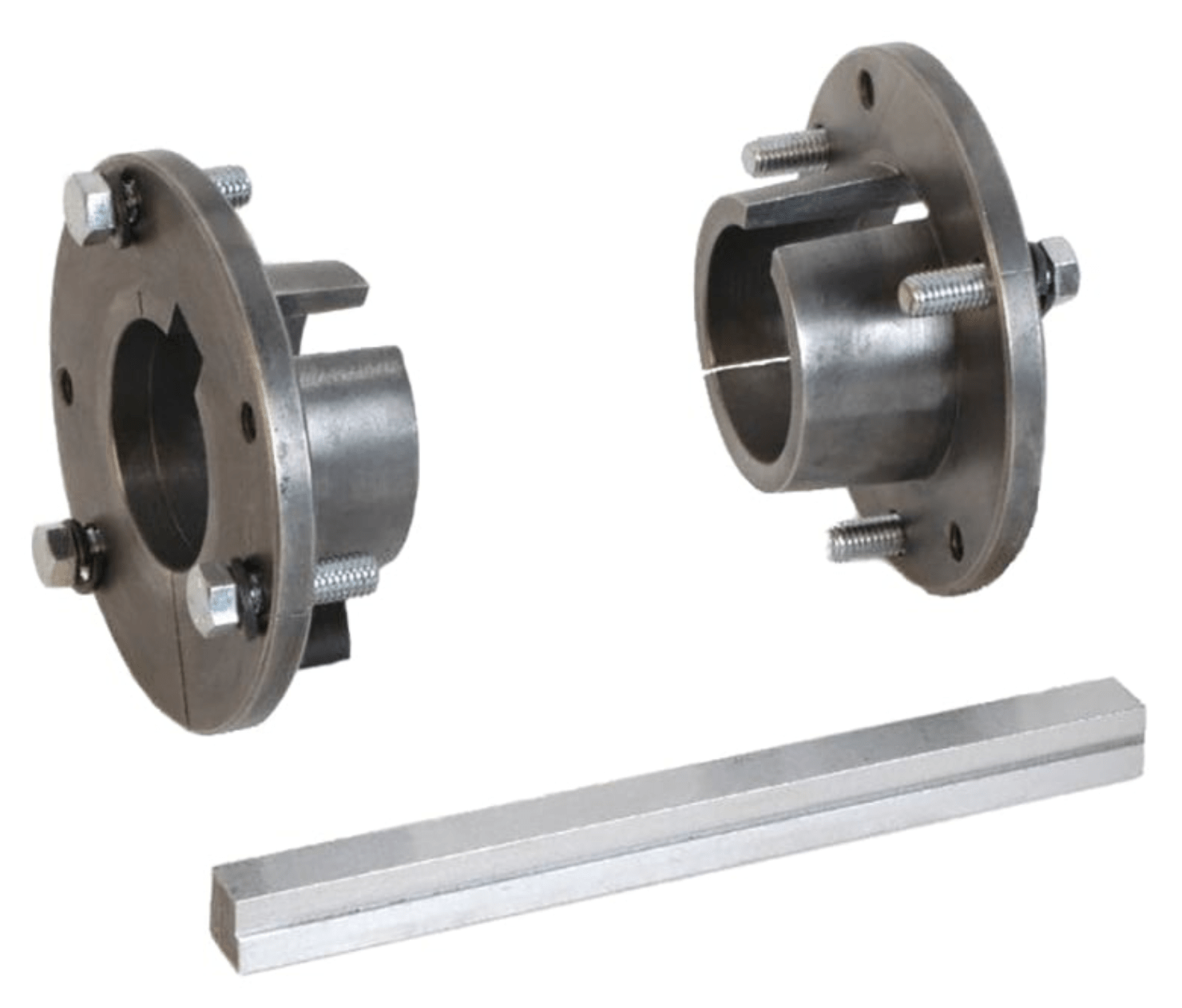
Fig B – Example – A typical standard twin tapered bushing kit available in many bore sizes such that one gearbox can accommodate various conveyor, head shaft diameters.
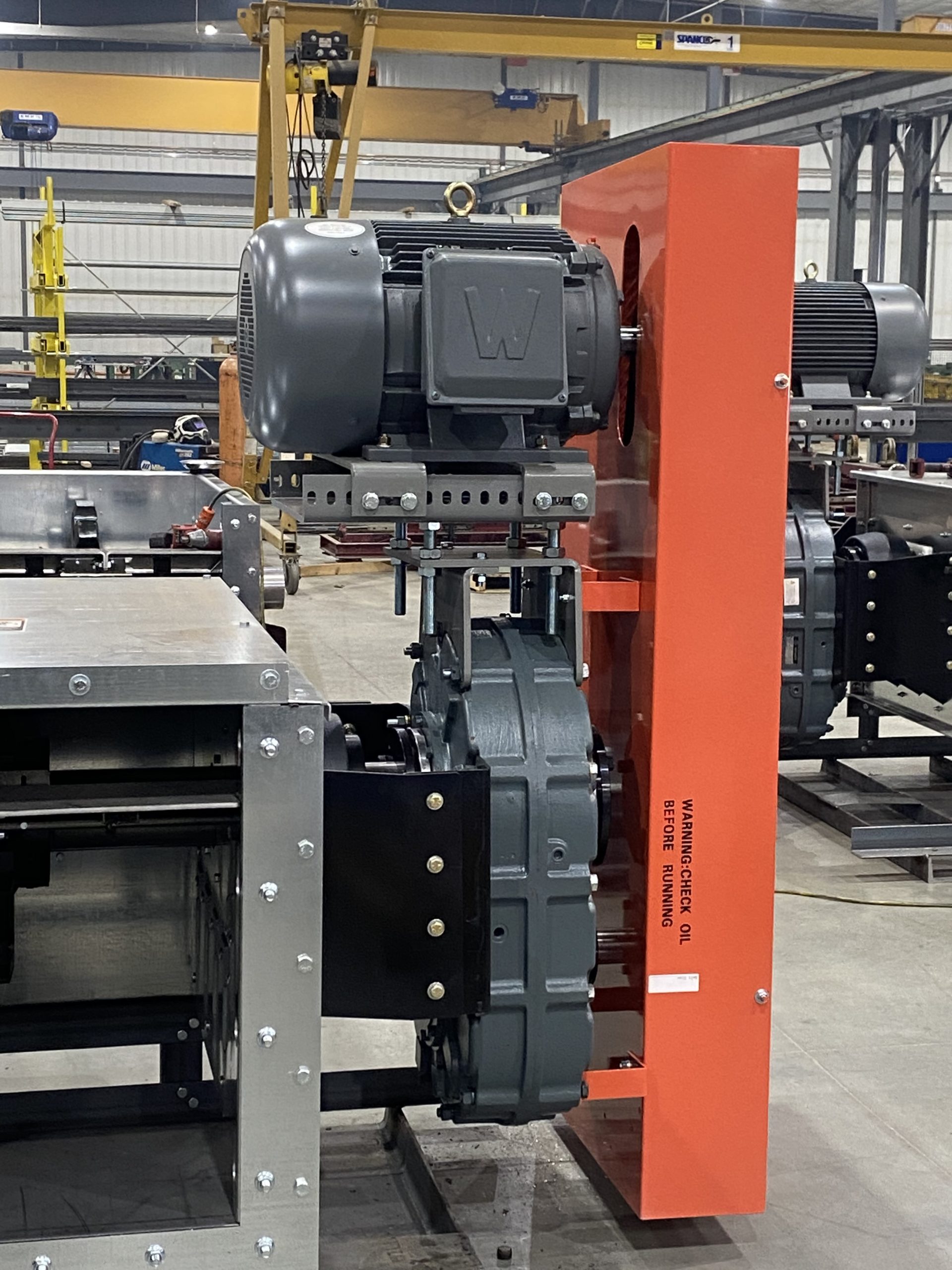

Fig A – Example – Gearbox and motor combination using v-belts under the protection of a belt guard.
Low Hanging Fruit to Reduce Risk
Many older gearboxes have yet to be replaced with modern, optimized equipment and installation accessories to obtain the desired ratios. Large, custom gearboxes with unique ratios are abundant and can be considered low-hanging fruit for a plant operator to prioritize. Many gear manufacturers no longer support legacy gearboxes, and the lead times are excessive if they can manufacture replacements. Replacing older non-standard units will reduce the likelihood of extended downtime.
Lean On Your Equipment Manufacturers
Find a supplier who will examine your application and provide an unbiased solution using standard, readily available equipment. Specifying gears for a given application and ensuring the correct loads, ratios, mounting, and operational durability requires special skill.
Worldwide Electric is among the best and most capable firms at providing dependable and cost-effective solutions. Our team of experienced salespeople, engineers, and specialists is readily available to consult with and provide cost-effective and reliable solutions for your conveying needs.
In Summary
Understand that your application and the associated environmental conditions will cause equipment failures. You can reduce the likelihood of failure by removing a factor you can control – Selecting the right product. Downtime is a significant cause of lost production (revenue). Equipment failure caused by one component may impact a more extensive system and drive additional equipment replacement costs. Utilizing the same equipment throughout your plant rationalizes maintenance and spare parts stocking methodology. Also, using versatile equipment with application accessories further simplifies stock-keeping and allows immediate repair when equipment fails. Preventative maintenance or replacement of unique or old equipment will reduce the likelihood of prolonged downtime should equipment fail. Lastly, find a supplier you can trust who picks up the phone when you call, offers unbiased advice, has in-stock availability of standard products, and can get that product to you quickly.

Author | Jeff Pangborn | National Sales Manage, Gearing | WorldWide Electric Corporation
Jeff has spent his entire 38-year career in the Power Transmission and Bearing Industry. Having worked for both distributors and manufacturers during this span. Jeff in particular has amassed a great deal of experience in the gearing segment. With his wealth of product knowledge and industry experience, Jeff supports Worldwide Electric’s vast network of industrial distributors, as well as providing training and application expertise to the Worldwide Electric Team.
